Google Analytics can be a great help in understanding and improving your website and channel performance. Leveraging the best Google Analytics features will get you ahead of your competition.
There are probably 50, 100 or even more features that I use on a regular basis.
Some of them relate to collecting relevant and reliable data in Google Analytics. Others are more geared towards meaningful analysis and gathering insights for the business.
But which ones are the most useful? It depends, but certainly there are a few that should be on top of your list!
 In this article I will present the top 25 features that I use daily for my clients.
In this article I will present the top 25 features that I use daily for my clients.
Table of Contents
1. Regular Expressions
I believe every Analyst and Marketer should have at least a basic understanding of how and why to use regular expressions.
Regular expressions are incredibly useful when:
- Setting up Google Analytics (and Google Tag Manager).
- Analyzing data in the GA reporting interface.
- Optimizing your website and channel performance.
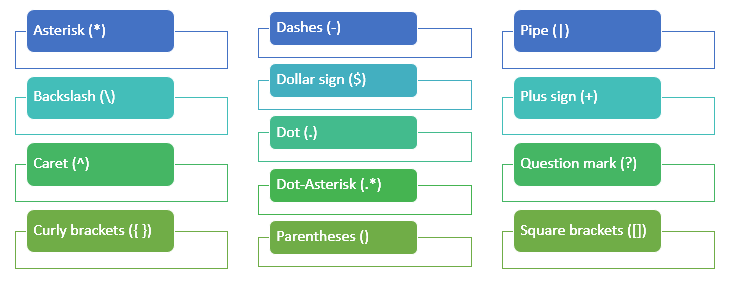
Reading suggestion: Ultimate Guide to Regular Expressions in Google Analytics.
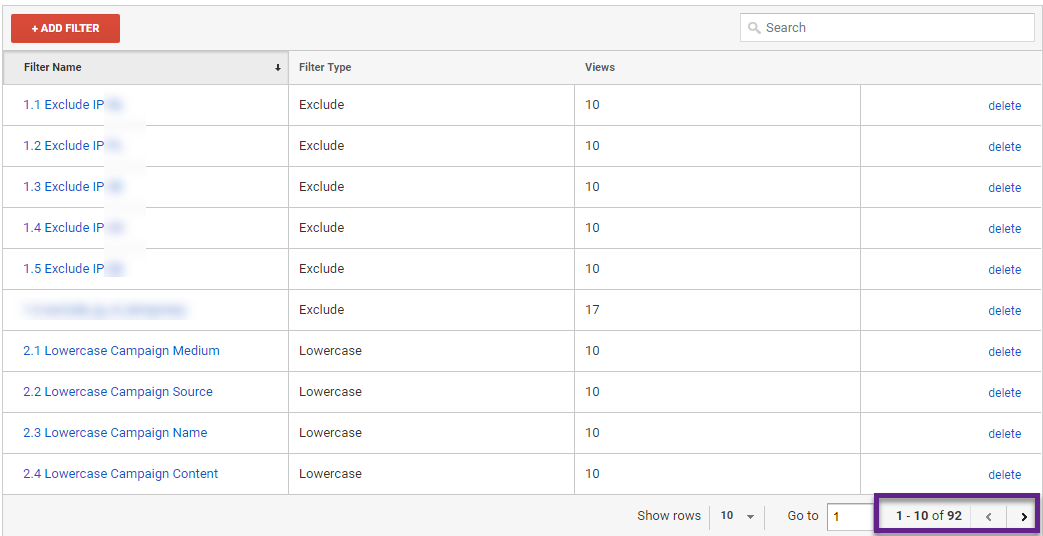
2. Filters
Google Analytics filters are your best friend if you want to have better control over the data that appears in each of your reporting views.
Three example use cases for configuring filters in Analytics:
- Exclude IP addresses of known visitors.
- Remove all query parameters at once (e.g. technical query parameters on Ecommerce sites).
- Ensuring utm parameters (traffic source parameters) are all shown in lowercase in Google Analytics (no duplicates).
 Reading suggestion: Ultimate Guide to Using Google Analytics Filters.
Reading suggestion: Ultimate Guide to Using Google Analytics Filters.
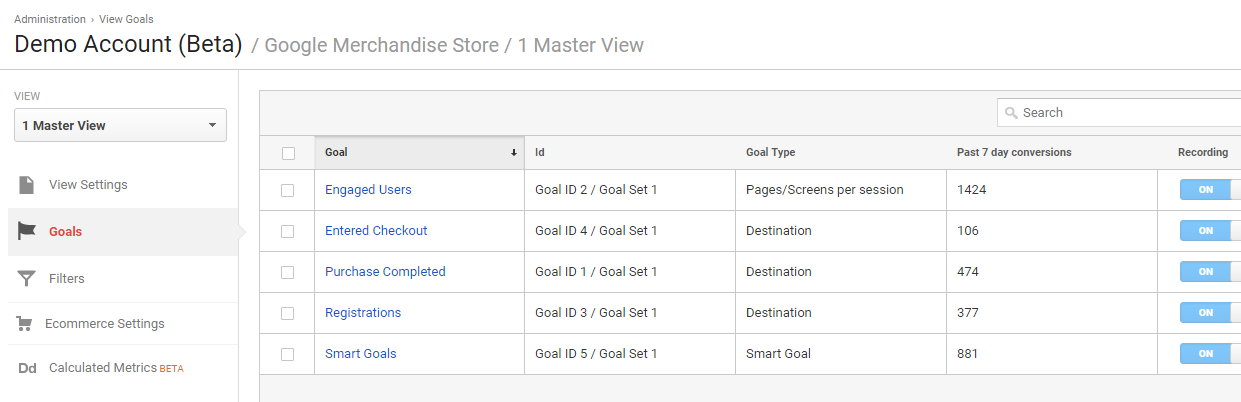
3. Goals
What do you want to accomplish? What do you want to improve?
Setting up a clear measurement plan and goals is of crucial importance for your business. Goals belong to the most important Google Analytics features.
In Google Analytics you have the option to set up 20 goals per reporting view (five goals per goal set). You certainly don’t have to use all 20 slots, but in general I recommend setting up at least three goals.
I love to use the definitions of:
- Macro goal(s): the most important goal(s) for your business.
- Micro goal(s): secondary goals for your business – that might help in achieving your most important (macro) goal(s).
 Reading suggestions:
Reading suggestions:
4. Goal Value
Especially for non-ecommerce websites it is crucial to define a goal value for one or more of your goals.
By doing this you will:
- Make your data analysis more meaningful.
- More quickly get an approval from your client or boss to take a certain action.
- Enjoy digital analytics much more!
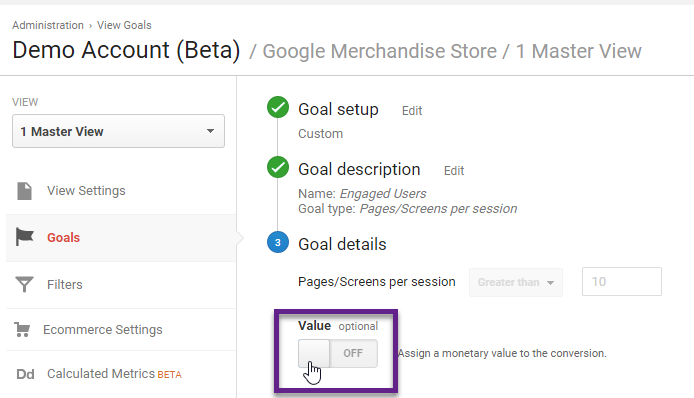
One exception, if you run an ecommerce site and/or have ecommerce enabled, you don’t want to set up a goal value in the ecommerce view. This will distort/inflate your value metrics.
Reading suggestion: The Importance of Goal Values in Google Analytics.
5. Calculated Metrics
As Daniel Waisberg pointed out in my Actionable KPI roundup, do not stick to the default metrics.
Google Analytics provides you with the opportunity to create your own set of metrics:
- Five additional, calculated metrics can be created in the free version of Google Analytics.
- Fifty in GA 360.
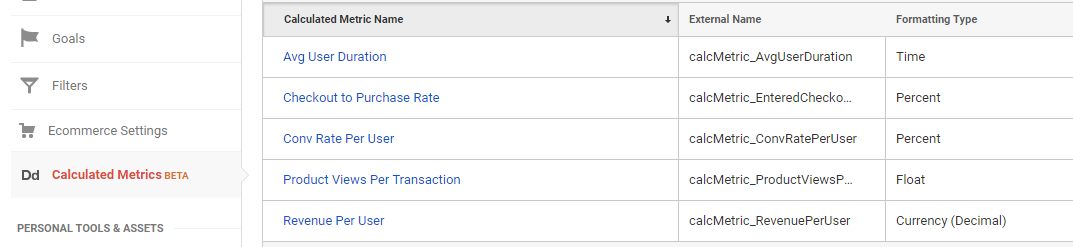
This is calculated per reporting view. In theory you could set up different views for the sole purpose of working with a ton of calculated metrics.
Calculated metrics are incredibly powerful for analysis and optimization. One big drawback is that they can’t be directly used via the Google Analytics API (yet).
Reading suggestion: Ultimate Guide to Calculated Metrics in Google Analytics.
6. Campaign Tracking
Most probably you spend a lot of money on acquiring traffic, e.g. via AdWords, Paid Social, Affiliate Marketing or Email.
This is ok as long as you know how each of these sources perform. The Acquisiton, Behavior and Conversion metrics (ABC) in Google Analytics should be accurate.
You will need to correctly tag all of your campaigns – in addition to those that are recognized on default.
![]()
Reading suggestion: Ultimate Guide to Google Analytics Campaign Tracking.
7. Channel Grouping
The two main ways to view, analyze and optimize your traffic is by looking at:
- Source/medium definitions.
- Channel group definitions.
I recommend using the default and custom channel grouping features for a holistic channel performance overview.
After, you can drill down at specific “source/medium” definitions to learn more.
It is important to note that you can only use the default channel grouping when using the Google Analytics API.
This is why I choose to modify the default channel group for my clients.
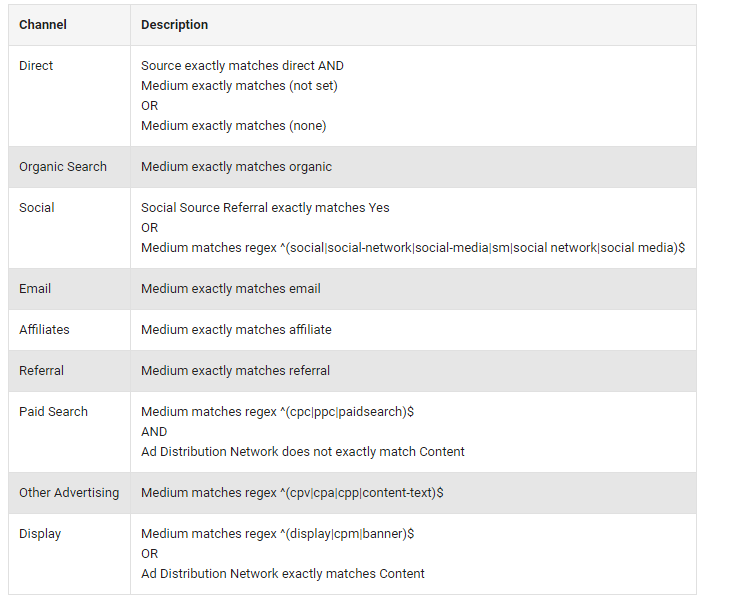 As you can see, the default channel group definitions are derived from source and medium parameters.
As you can see, the default channel group definitions are derived from source and medium parameters.
Getting your channel grouping setup right is not a one-time exercise. You need to review the setup on a regular basis to ensure you keep on collecting reliable data in your Google Analytics account.
Reading suggestion: Google Support Doc About Channel Groupings.
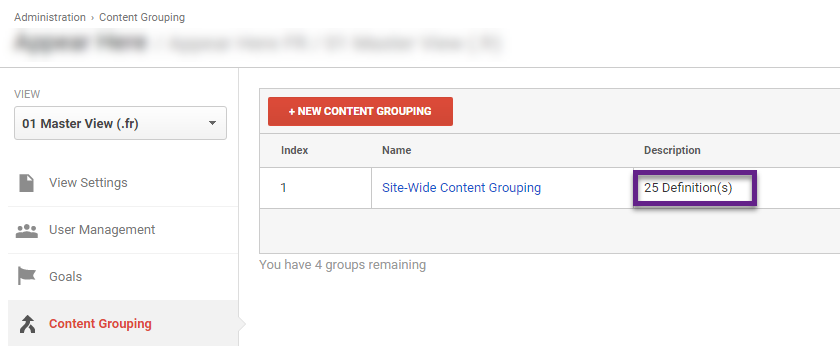
8. Content Grouping
Do you know exactly how each of your website sections perform?
Content Groupings are very powerful in structuring and analyzing your content performance in a smarter way.
On default, Google Analytics shows you all the different pages that have received at least one pageview in the selected period.
A website that contains hundreds or maybe thousands or even more unique pages will greatly benefit from setting up content groupings in Google Analytics.
This allows you to better perform:
- In-depth, aggregate navigational behavior analysis.
- Pre-research for Conversion Optimization.
- Content and page value analysis.
Your exact needs depend on your website and type of business. In general, I recommend to always set up a site-wide content grouping.
“A site-wide content grouping covers at least 98% of all pageviews on your website and divides all pageviews into logical buckets for aggregated navigational and performance analysis and optimization.”
 Reading suggestion: The Complete Guide to Google Analytics Content Groupings.
Reading suggestion: The Complete Guide to Google Analytics Content Groupings.
9. Site Search
Most websites have an internal Site Search module embedded on their site.
I have found in my Google Analytics Audits that many websites haven’t set up Site Search at all or incorrectly. For a ton of reasons you want to leverage this Google Analytics feature:
For a ton of reasons you want to leverage this Google Analytics feature:
- Discover profitable keywords for SEO.
- Discover profitable keywords for PPC.
- Expand your product assortment or services.
- Optimize experience/performance of Site Search visitors.
- Optimize technical Site Search performance.
Bonus: you can even utilize this feature if your website doesn’t contain a Site Search functionality. Most websites contain specific query parameters and – instead or in addition to segments – you can use Site Search to analyze the performance of a specific subset of visitors. You can add one or more non-Site Search query parameters to this field instead.
Reading suggestion: Five Terrific Insights via Google Analytics Site Search.
10. Event Tracking
Two common ways to track user interactions are pageviews and events.
Pageviews are great and the foundation of many reports in Google Analytics.
However, if you want to measure and learn from what happens on a page, you want to use event tracking.
I have encountered many Google Analytics setups where events where:
- Not configured / coming through in GA.
- Incorrectly configured.
- Incompletely configured (due to the lack of a concise measurement plan).
You need to learn about and implement event tracking on your website if you want to help your visitors achieve their goals and increase the positive impact and ROI of your business.
![]()
11. Segments
Data analysis and optimization insights are hidden in segments. Aggregate data analysis is a good start, but make sure to dive deeper.
This is when Google Analytics segments are extremely valuable.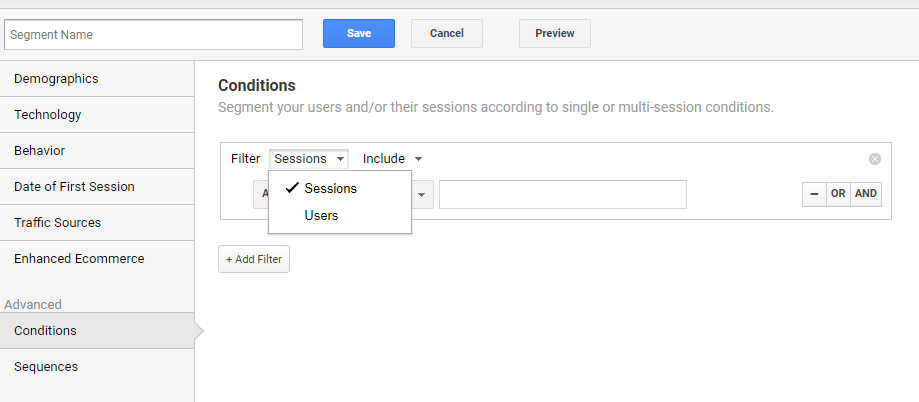 You can define your own segments or use one of the predefined segments already available in Google Analytics.
You can define your own segments or use one of the predefined segments already available in Google Analytics.
Segments belong – in my opinion – to the top three Google Analytics features for Google Analytics data analysis and optimization.
And I have already written quite a few articles about how to best leverage them.
Reading suggestions:
- In-Depth Overview of Different Google Analytics Segments.
- How to Leverage Sequence-Based Segments in Google Analytics.
- 10 Differences Between View Filters and Segments.
12. Secondary Dimensions
As mentioned before, placing your aggregated data in perspective and further drilling-down, is the way to find greater insights for your business.
One simple, but very effective way to gain better insights is by applying secondary dimensions.
In most Google Analytics reports this extra dimension is available. Here is an example: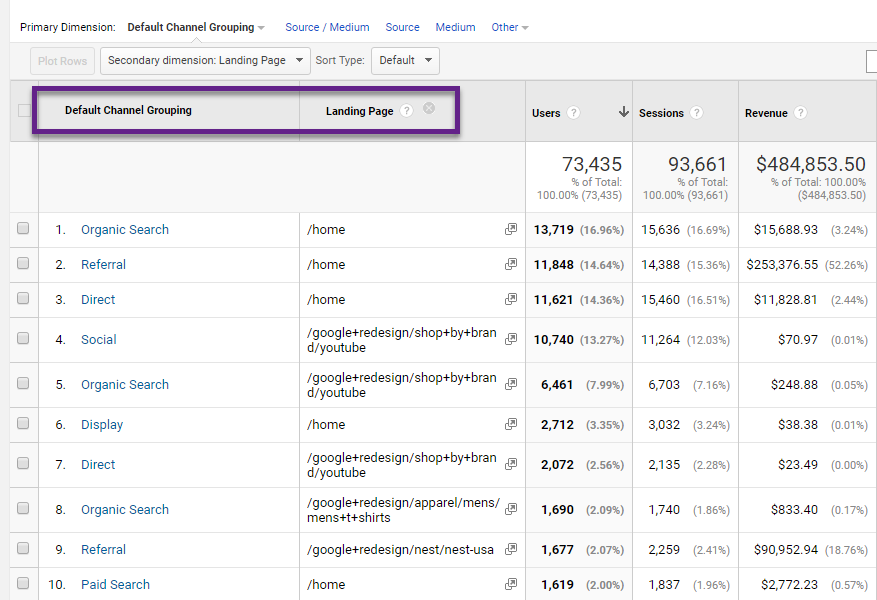 The report above includes two dimensions:
The report above includes two dimensions:
- Primary dimension: Default Channel Grouping.
- Secondary dimension: Landing Page.
Reading suggestion: How to Boost Your Data Insights with Secondary Dimensions.
13. Custom Dimensions
Secondary dimensions can be applied without having to modify your implementation or configuration.
However, they are limited as you can only choose pre-defined dimensions.
Custom dimensions allows you to attach useful, additional information to hit, session, user and product data that you can send to Google Analytics.
This is very useful for most businesses out there. The downside is that you need a solid technical backgroud (or someone who can help) to properly implement this feature.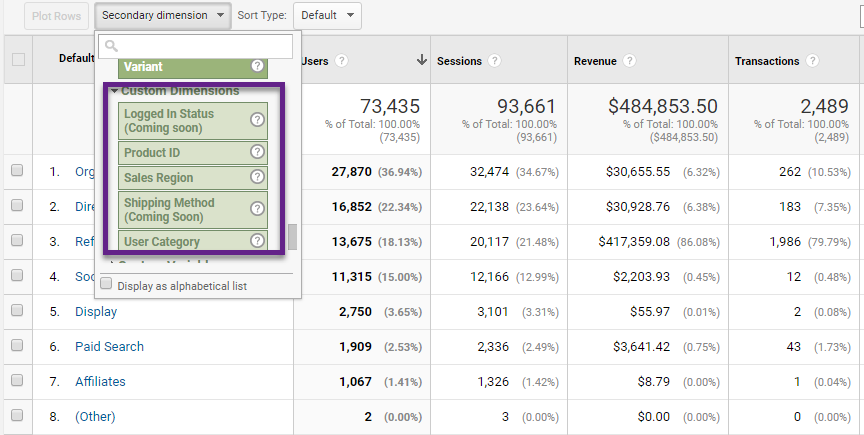 You can make them useful in multiple ways:
You can make them useful in multiple ways:
- Build custom reports with your custom dimension as a primary dimension.
- Apply them as secondary dimensions to your standard/custom reports.
- Query them via the Google Analytics API.
Reading suggestion: How to Leverage Custom Dimensions in Google Analytics.
14. Custom Metrics
Custom metrics belong to the most underused features in Google Analytics.
In Google Analytics there are three types of metrics:
- Pre-defined metrics.
- Calculated metrics.
- Custom metrics.
Similar to custom dimensions, custom metrics can have different scopes: hit-level and product-level scope.
They are incredibly powerful as you can add them to any report or dashboard. Further, they can serve as input for calculated metrics.
Reading suggestion: Complete Guide to Leverage Custom Metrics in Google Analytics.
15. Real-Time Reporting
The real-time report section in Google Analytics is very effective for many reasons:
- Directly monitor the effect of one-day campaigns.
- Monitor goal completions as you make changes on your site.
- Verify that your tracking code is working properly.
- Verify utm link tracking.
And there are many more reasons why you should use these reports: Reading suggestion: The Marketer’s Guide to Real-Time Reports in Google Analytics.
Reading suggestion: The Marketer’s Guide to Real-Time Reports in Google Analytics.
16. Google Analytics Add-Ons
Google Analytics can do a lot to your business, but you should go the extra mile by leveraging all the great add-ons/tools that are available.
They are great in increasing your data quality and productivity.
I have written an extensive article that goes in much about the Google Analytics Tools that are available.
It describes the most popular debugging as well as reporting/analysis tools.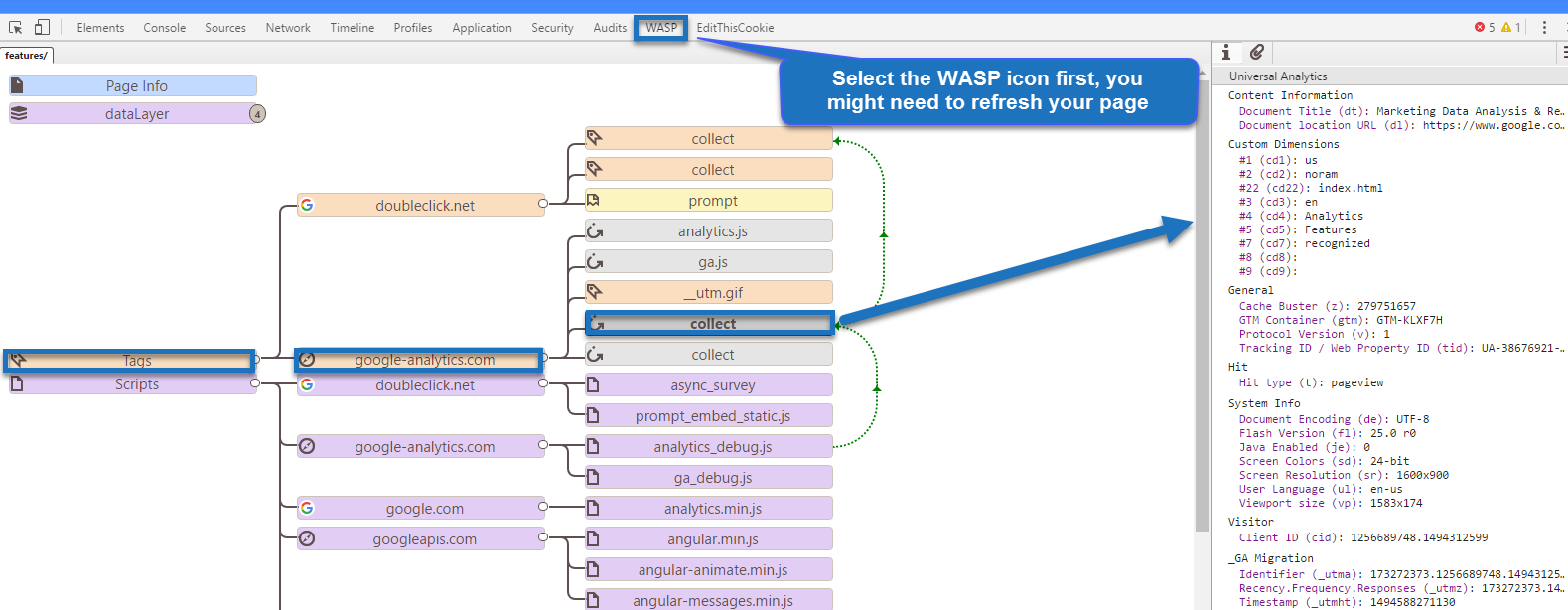 Reading suggestion: Top 15 Google Analytics Tools to Improve Data Quality and Productivity.
Reading suggestion: Top 15 Google Analytics Tools to Improve Data Quality and Productivity.
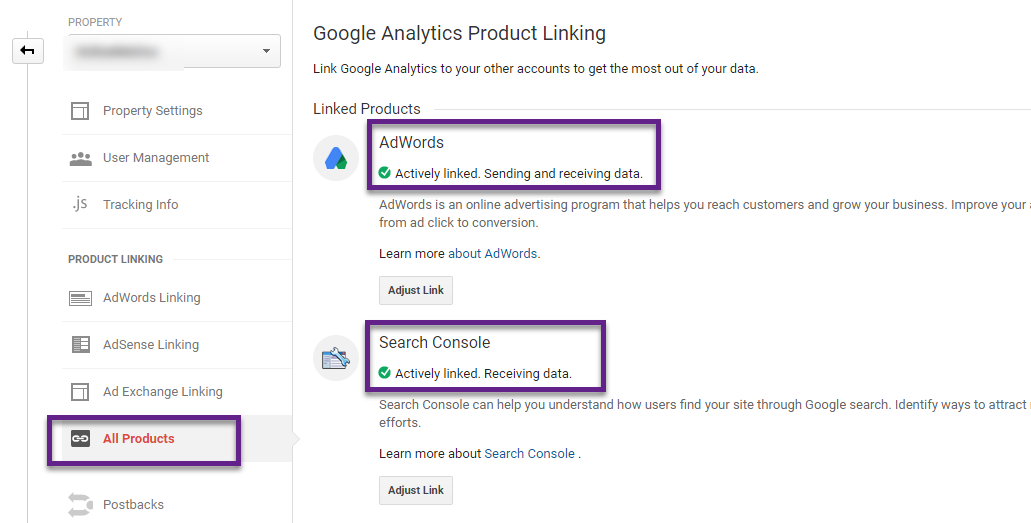
17. Google Analytics Integrations
In addition, you can integrate Google Analytics with dozens of Google and Non-Google products, a few examples:
- AdWords
- AdSense
- Search Console
- YouTube
- Qualaroo
At a minimum, I recommend to integrate Google Analytics with AdWords and Search Console.
Reading suggestion: Ultimate Guide to Google Analytics Integrations.
18. Custom Reports
Every business is different and should use the Google Analytics data to their advantage.
In my experience, you will have the most flexibility when building your reports and dashboards outside of Google Analytics. Google Data Studio is a good option in most cases.
However, for quick (internal) needs you want to leverage the Google Analytics interface in the best possible way. That’s when custom reports can be really handy.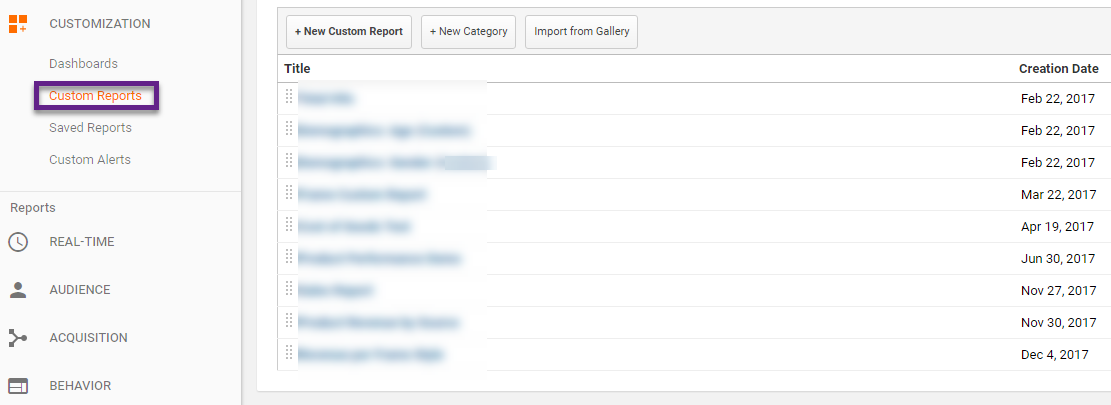 They are easy accessible and can be shared with other people who have GA access.
They are easy accessible and can be shared with other people who have GA access.
I have extensively used this feature in Google Analytics to help my clients access their most important data whenever they need.
Reading suggestions:
- Three Unique Ways to Create Custom Reports in Google Analytics.
- How to Avoid Common Pitfalls When Analyzing Custom Report Data.
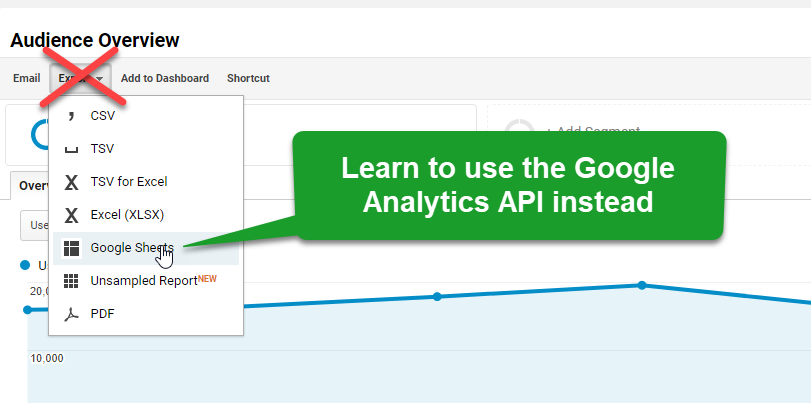
19. Google Analytics API
I am often asked to help companies automate their reporting efforts. With the goal of freeing up more time for data analysis and optimization.
Using the Google Analytics API is one of the smartest ways to efficiently work with your data.
You can either use the Google Analytics API to bring data into Google Analytics or get data out of Google Analytics. As simple as that!
 Every business can greatly benefit from using the Google Analytics API. So, start today I you haven’t used it yet!
Every business can greatly benefit from using the Google Analytics API. So, start today I you haven’t used it yet!
Reading suggestions:
- Google Analytics API: The Non-Technical Guide.
- 10 Actionable Tips to Master Metrics and Dimensions in Google Analytics.
- 8 Tips to Evolve From Reporting Squirrel to Analytics Ninja.
20. Annotations
Do you document when a new campaign starts or when you change a goal in Google Analytics?
Keeping track of the most important activities that might impact your data is very important to do.
Only then you can place your data in perspective, analyze it in the right context and draw relevant conclusions. Google Analytics comes with a feature called Google Analytics annotations that can be a great help.
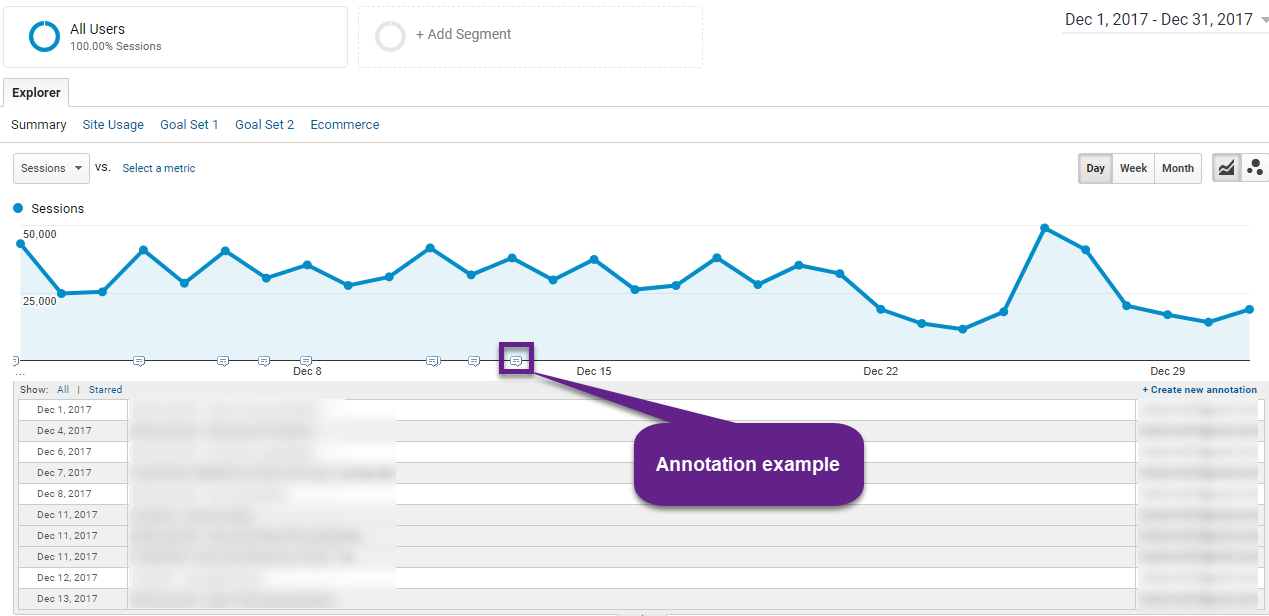 Reading suggestion:
Reading suggestion:
21. Custom Alerts
You cannot keep track of everything that happens in your account by manually monitoring it. And even if you could, you shouldn’t do it.
It’s much more effective to use the tools available to alert you when something unexpected happens or goes wrong.
That is when alerts in (and outside of) Google Analytics really come in handy.
You can automatically monitor certain changes in your data that are important to take action on.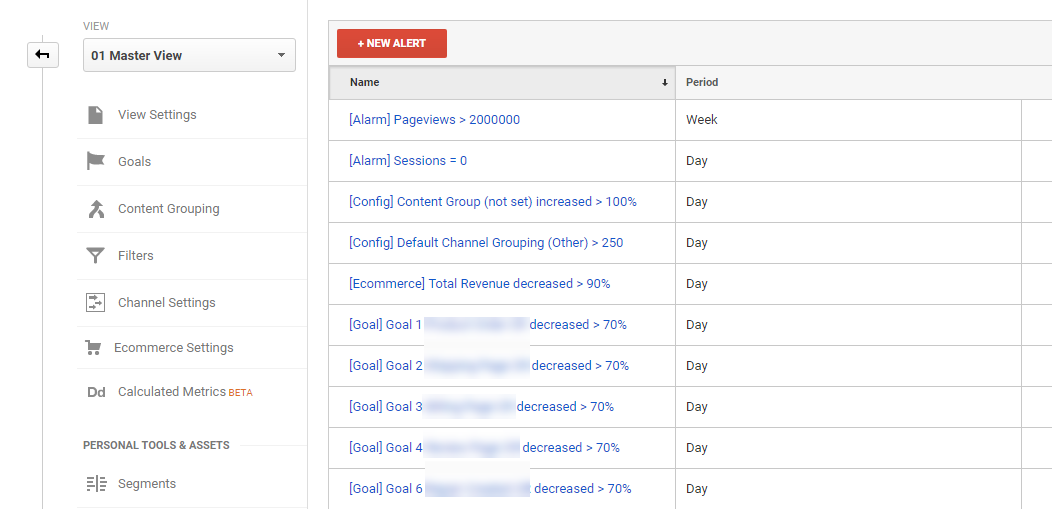 These alerts are set up in the admin section of Google Analytics. And as you can see I like using naming conventions whenever possible.
These alerts are set up in the admin section of Google Analytics. And as you can see I like using naming conventions whenever possible.
Reading suggestion:
- How to Use Google Analytics Annotations for Better Insights.
- How to Leverage Custom Insights in Google Analytics 4.
22. Analytics Intelligence
Machine learning is growing and establishing itself in many different ways and industries.
Google Analytics has introduced the “Analytics Intelligence” feature not too long ago.
Contrary to Custom Alerts – where you define your own events – Analytics Intelligence goes one step further. It crawls through your data and reveals insights on major changes or opportunities you should be aware of.
It can already be helpful for some and I expect this feature in Google Analytics becoming more useful in the near future.
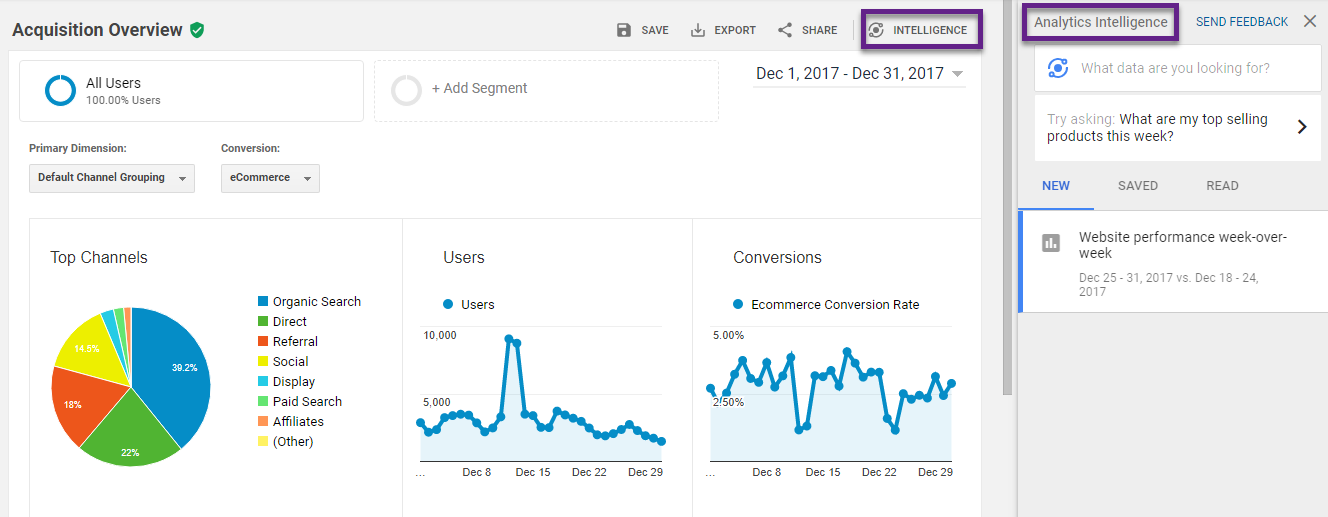 Make sure to stay informed and try out these new tools now and when they involve over time.
Make sure to stay informed and try out these new tools now and when they involve over time.
Reading suggestion: Ask Analytics Intelligence.
23. Shortcuts
Segmenting on date range or time period can bring a lot of insights. How does my website or a particular channel perform compared to last month?
The Google Analytics shortcuts feature is very handy in this case: press SHIFT + ‘?’ keys on your keyboard.
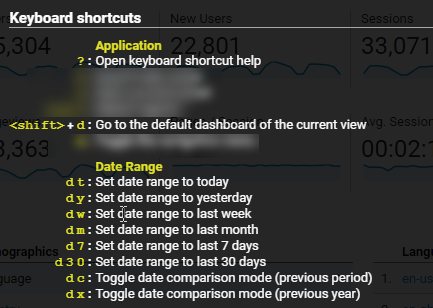
Go ahead and try! I have heard many people not to know yet about this feature.
24. Enhanced Ecommerce
In the past, the Ecommerce module and reports in Google Analytics were rather limited, but with the Enhanced Ecommerce module this has radically changed.
And the great thing is, you can leverage this module on Ecommerce and non-Ecommerce sites!
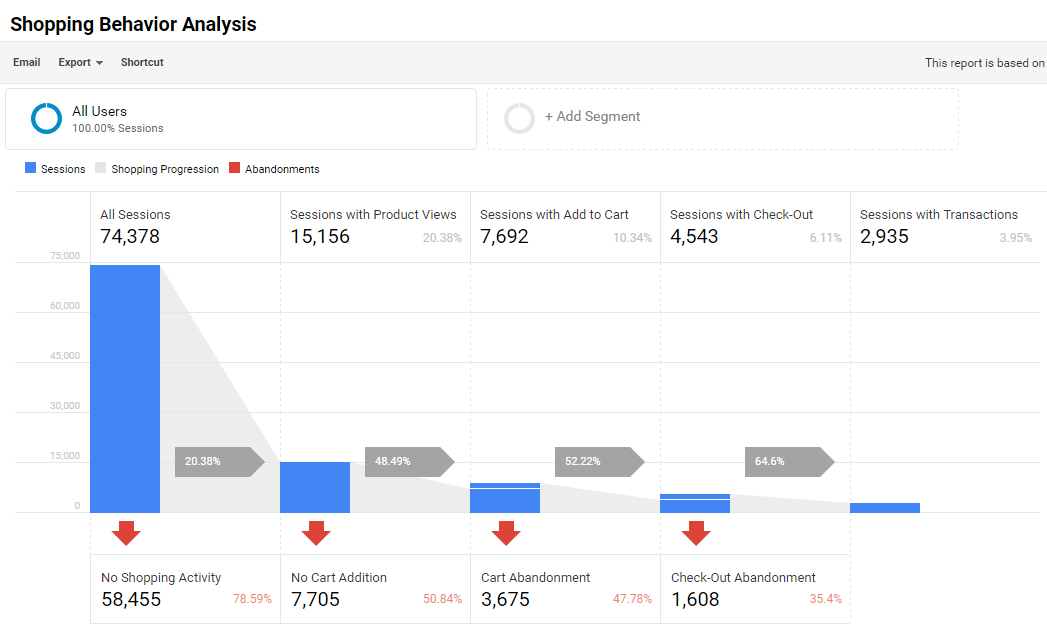 Reading suggestions:
Reading suggestions:
- Top 15 Enhanced Ecommerce Implementation Best Practices and Tips.
- 33 Google Analytics Insights from Enhanced Ecommerce and Segmentation.
25. Attribution
Last but not least, conversion attribution. On purpose I wanted to talk about this as the last thing in this post. This is because many companies I encounter start with attribution without getting the basics right first. Attribution is complex and requires advanced Analytics knowledge. It should never be the starting point in your organization.
As most of us know, the Google Analytics conversion model is based on last click/cookie performance. And this is far from optimal as you will see this working through in most reports that are available.
I challenge you to go one step further – if you are ready – by going beyond the last click performance model.
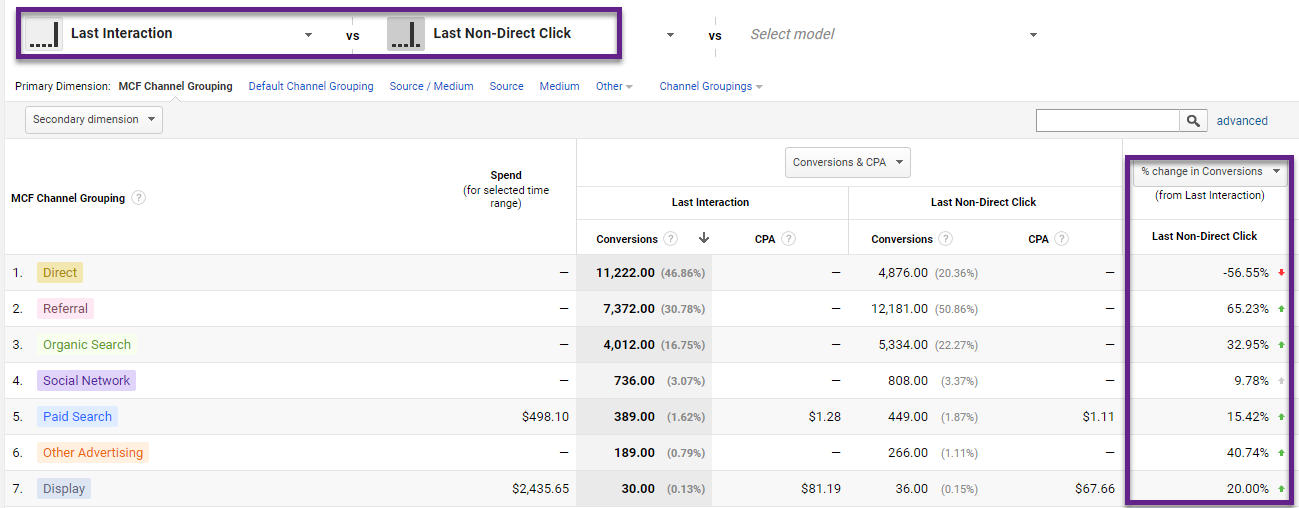
Reading suggestions:
- Complete Guide to Multi-Channel Funnels in Google Analytics.
- Which Google Analytics Attribution Model Should I Use?
There you have it, 25 Google Analytics features you should leverage for your business!
What do you think? Which feature(s) in Google Analytics do you use the most? Would be awesome to hear your thoughts here!
One last thing... Make sure to get my automated Google Analytics 4 Audit Tool. It contains 30 key health checks on the GA4 Setup.
Thanks Paul!
Your posts are greats, I really love read your blog.
Thanks for the heads up!